The Earliest Stage of Embryos Show Specialized Asymmetry
Research News
|
Dec 3, 2025


As nearly one in six couples experience fertility issues, in-vitro fertilization (IVF) is an increasingly common form of reproductive technology. However, there are still many unanswered scientific questions about the basic biology of embryos, including the factors determining their viability, that, if resolved, could ultimately improve IVF's success rate.
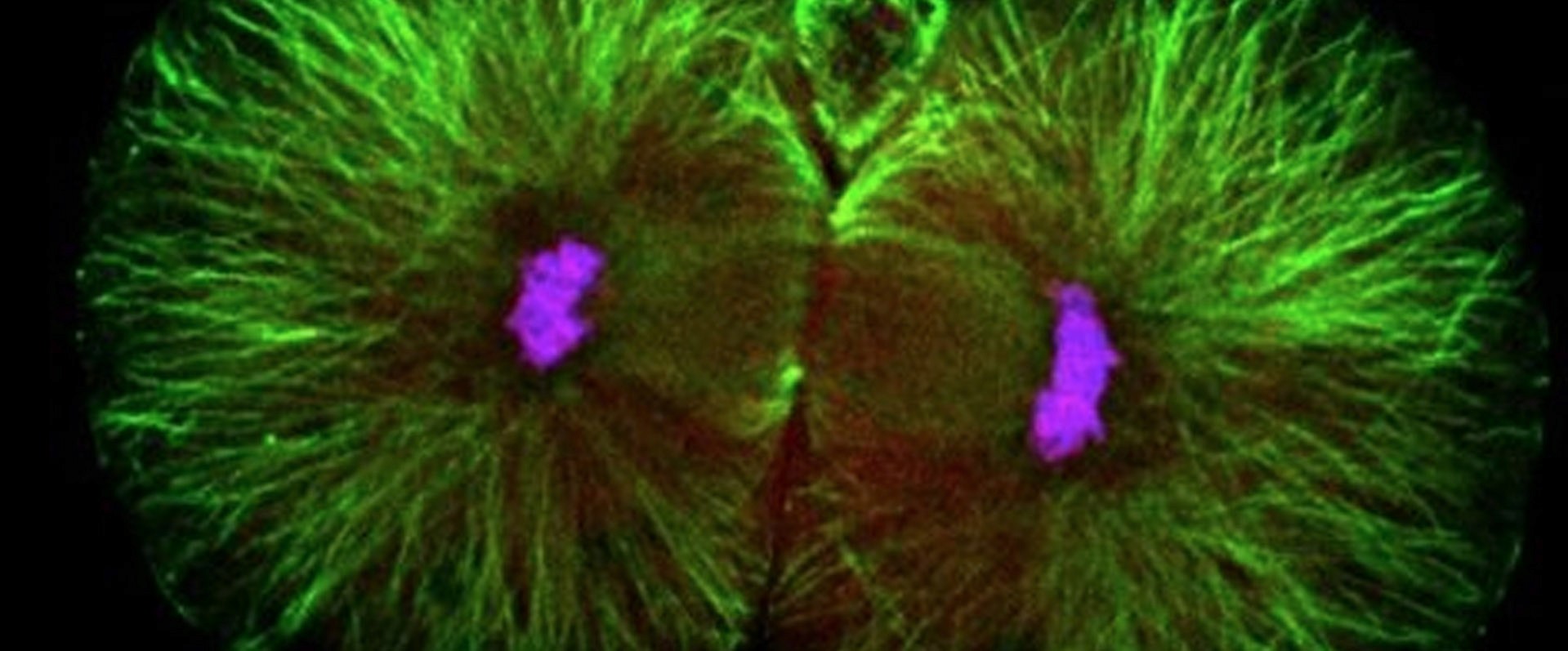
A new study from Caltech examines mouse embryos when they are composed of just two cells, right after undergoing their very first cellular division. This research is the first to show that these two cells differ significantly—with each having distinct levels of certain proteins. Importantly, the research reveals that the cell that retains the site of sperm entry after division will ultimately make up the majority of the developing body, while the other largely contributes to the placenta.
The research, conducted primarily in the laboratory of Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz, Bren Professor of Biology and Biological Engineering, and is described in a study appearing in the journal Cell on December 3.
As nearly one in six couples experience fertility issues, in-vitro fertilization (IVF) is an increasingly common form of reproductive technology. However, there are still many unanswered scientific questions about the basic biology of embryos, including the factors determining their viability, that, if resolved, could ultimately improve IVF's success rate.
A new study from Caltech examines mouse embryos when they are composed of just two cells, right after undergoing their very first cellular division. This research is the first to show that these two cells differ significantly—with each having distinct levels of certain proteins. Importantly, the research reveals that the cell that retains the site of sperm entry after division will ultimately make up the majority of the developing body, while the other largely contributes to the placenta.
The research, conducted primarily in the laboratory of Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz, Bren Professor of Biology and Biological Engineering, and is described in a study appearing in the journal Cell on December 3.



